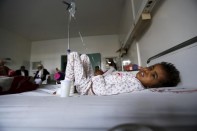
Marwan Ali Rajeh, 7, lies on a hospital bed while being treated for injuries he suffered from a Saudi-led air strike that killed two of his brothers near Sanaa, Yemen, June 24, 2015. REUTERS/Khaled Abdullah
Eight-year-old Abdullah Ali lay screaming in pain in a Sanaa hospital on Wednesday as a doctor cleaned his torn face, the victim of a worsening war that threatens millions of Yemenis with starvation and homelessness.
“We were at home when air strikes hit the missile base on the mountain near our house,” Abdullah’s father Musleh said by his bedside, describing an air raid on an arms depot a month ago that sent missiles raining across part of Yemen’s capital.
“Shells from the base started flying over the houses. We tried to make our escape but, when we were in the street, a piece of shrapnel hit my son. Thank God the doctors were able to remove it, but he needs more help.”
A country that was already by far the poorest and most unstable on the Arabian Peninsula is now, after three months of conflict, in the grip of a humanitarian disaster.
Cut off from the world, living under bombardment from a Saudi-led coalition and beset by fighting between multiple battalions and militias, Yemen’s 25 million people are prey to hunger, disease and an ever-present fear of death.
“The most terrifying thing, worse than anything we’ve suffered in this war, is the indiscriminate shelling that
falls on us every day,” said Saleh Hashem, a retired teacher from Aden.
In war-torn districts of the southern port city, mountains of rubbish fester in heat of over 40 degrees Celsius (104 Fahrenheit), helping to fuel an outbreak of dengue fever that has infected over 3,000 people nationwide, according to the United Nations.
TANKS AND SNIPERS
Snipers flit across rooftops and tanks heave into the abandoned streets, spitting out shells seemingly around the clock as residents huddle indoors.
“You don’t know where it will come from, and you know it could kill you and your family any moment, just as it kills women and children every single day,” Hashem said.
When Yemen’s now-dominant Houthi movement advanced toward Aden in late March, a Saudi-led alliance of Arab states began bombing in a bid to restore the elected president, who is backed by Saudi Arabia and has fled to Riyadh.
While the intervention held up the Houthi advance, it failed to push the militia back again, leaving large numbers of civilians trapped between battle lines across southern Yemen.
The Houthis say their advance is part of a revolution against a corrupt government and against Islamic militants.
Saudi Arabia, determined to thwart any arms deliveries to the Houthis, has imposed a near total blockade on a country heavily reliant on imports, reducing supplies of food, fuel and medicine to a trickle. Some families are breaking their daily fast for the Muslim holy month of Ramadan - meant to be a time of joy and plenty - with rice, bread and canned fish.
And, after a wave of deadly car bomb attacks claimed by Islamic State on mosques in Sanaa, many of the faithful in the capital say their prayers at home.
Three thousand have perished in the war, over a million have fled their homes and more than half of the population do not have reliable access to food, according to U.N figures.
“Yemen is also dependent on imports for 90 per cent of its food. What food and fuel does make it in is then not being distributed to where it is needed, because it is blocked by fighting on the ground,” Britain’s international development secretary, Justine Greening, said this week.






